Traditional data sharing methods are becoming increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats. These vulnerabilities stem from several factors, including the rise of quantum computing, which poses a significant risk to current encryption standards.
Additionally, sensitive data may be exposed during processing due to a lack of encryption, and weak access controls can allow unauthorized users to gain access to confidential information.
Quantum computing poses a threat to traditional encryption algorithms like RSA and ECC, as it can efficiently solve complex problems that underpin these methods, rendering them insecure.
Sensitive data transmitted or processed without strong encryption remains exposed to interception, leaving it vulnerable to unauthorized access or manipulation.
Weak or static access control mechanisms fail to enforce granular permissions, allowing unauthorized users to access sensitive information.
Ineffective or outdated authentication processes can inadvertently reveal sensitive personal information during identity verification.
Failure to adhere to data protection regulations results in gaps in security practices, increasing the likelihood of data breaches and legal repercussions.
Logging systems that lack integrity and tamper-resistance are prone to manipulation, making it difficult to detect security incidents or trace unauthorized actions.
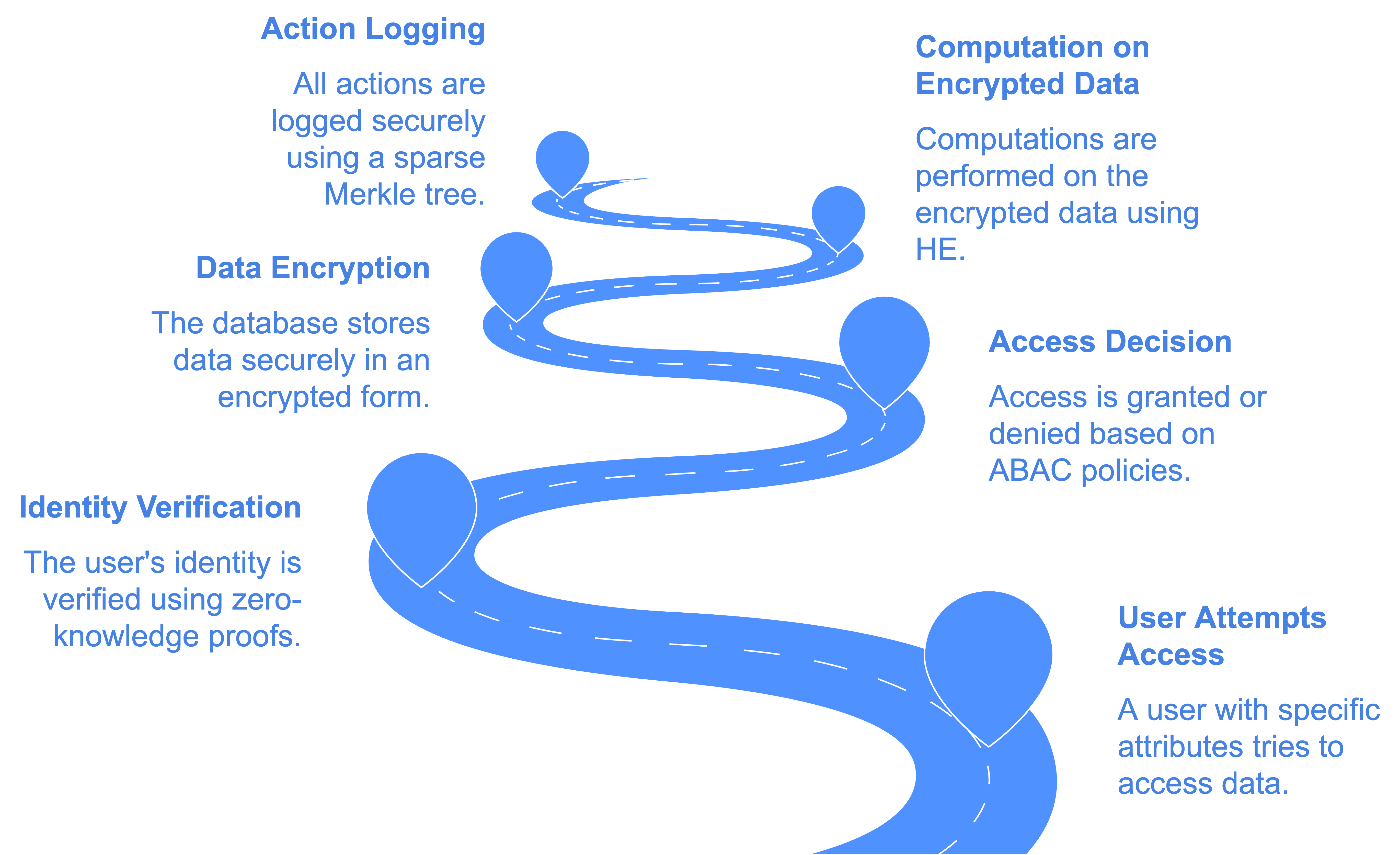
The Secure Data Access Process is designed to safeguard data privacy and security at every stage. It begins with zero-knowledge proof identity verification, ensuring user authenticity without compromising sensitive information. Data is then encrypted and securely stored, while all operations are logged for transparency and accountability.
To enhance security further, Homomorphic Encryption enables computations on encrypted data, preventing data exposure during processing. Attribute-Based Access Control strictly limits access to authorized users, ensuring that only verified individuals can interact with the protected information.

Post-quantum cryptography refers to cryptographic algorithms that are secure against the potential threats posed by quantum computers
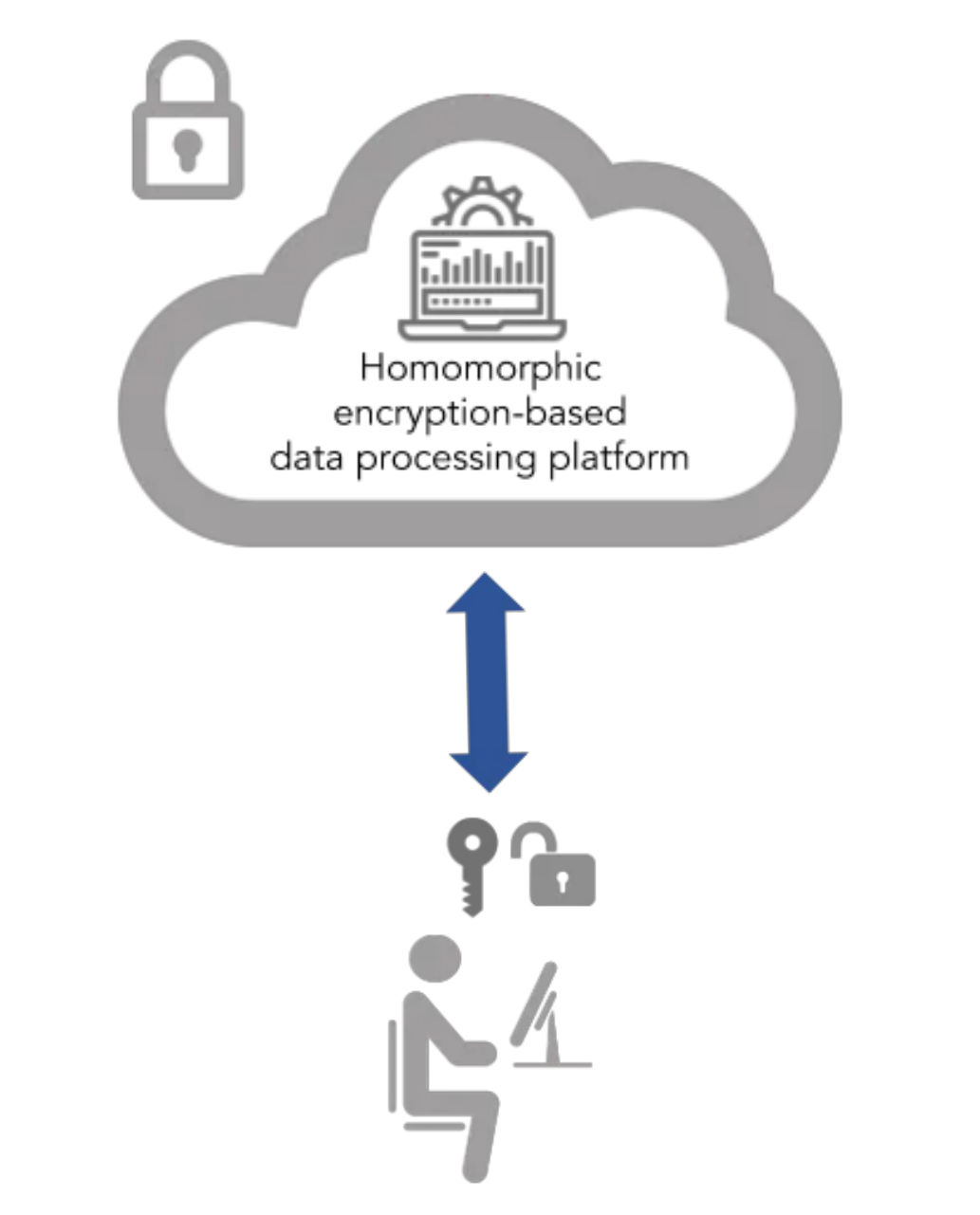
Allows computations on encrypted data without decryption. The result, when decrypted, matches the computation on the original data.

Allows one party to prove to another that they know a value without revealing the value itself.

Grants access to resources based on attributes of users, resources, and environments.

Uses cryptography for secure, verifiable, and auditable digital records.

Learn more about our advanced technologies and how they can help you transition from insecure to secure data sharing.
